|
License requirements: Layout and AXIEM (MWO_105+, XEM_001, XEM_100 or TOK_100)
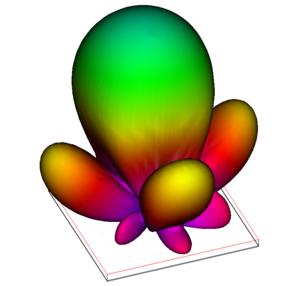
- In the "Principal Plane Cut Total Power" graph; note the principal plane cut; the steering angle (theta) is 9 degrees at 2.6 GHz.
- Rotate the 3D View of the antenna so the orientation matches that of the Principal Plate Cut Total Power by pressing the Back button
 on the EM 3D Layout toolbar. on the EM 3D Layout toolbar.
|